Electrical Theory & Applications for HVACR
Chapter 2: Circuits and Their Components
Page 33
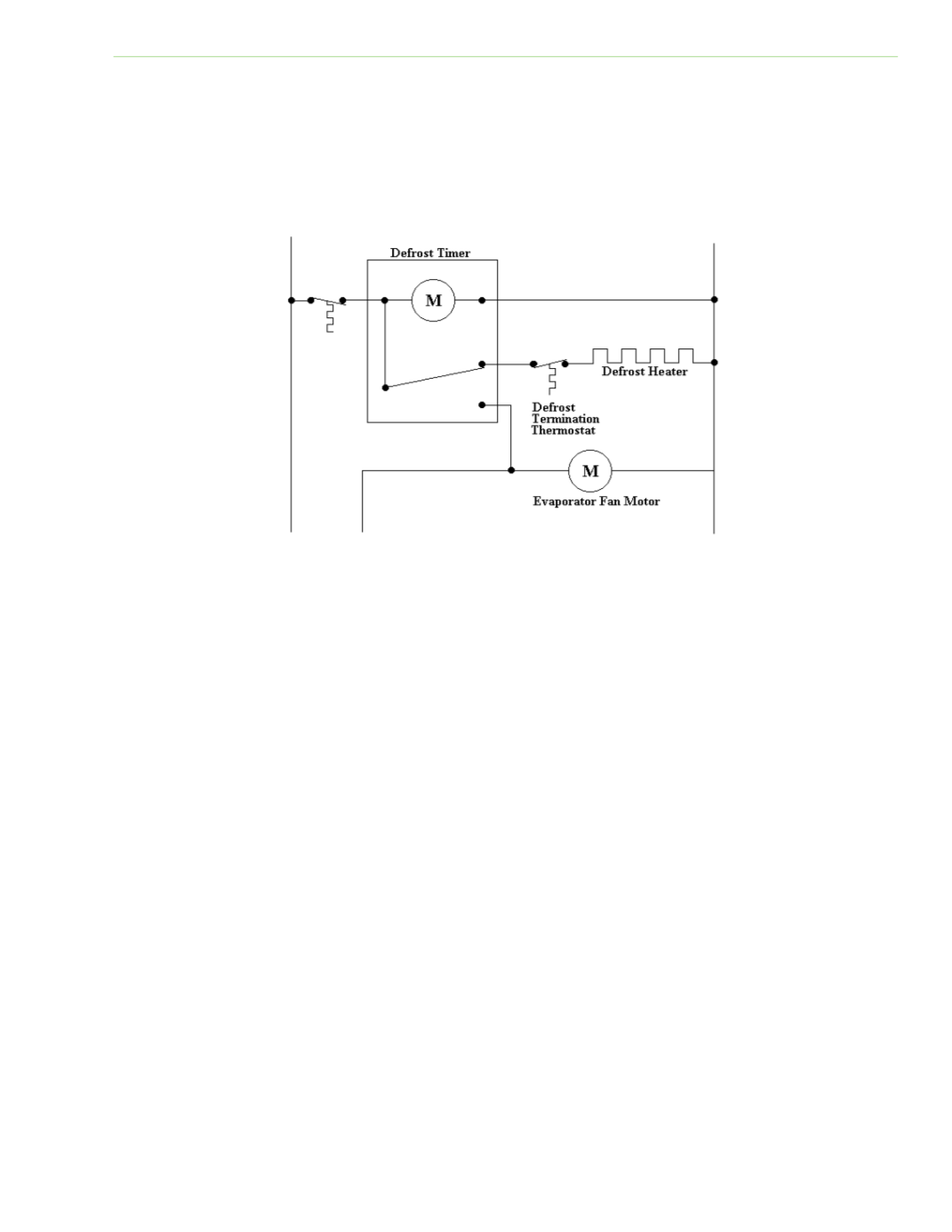
DEFROST TIMERS
To provide automaƟc defrosƟng of the evaporator coil, an electric heaƟng element energized by a
defrost Ɵmer may be located near the evaporator. A defrost Ɵmer is operated by a synchronous
motor like those used to operate wall clocks. A cam that is gear‐driven by the motor operates a set of
electrical contacts. At the proper Ɵme, these contacts change posiƟon, stopping the cooling process
and energizing the defrost heater or hot gas solenoid valve.
The synchronous motor in the Ɵmer can be wired in two ways: as a conƟnuous‐run Ɵmer or as a
cumulaƟve compressor‐run Ɵmer. In the conƟnuous‐run mode, the Ɵmer is wired directly across the
power source and operates on a conƟnuous basis. In cumulaƟve compressor‐run mode, the Ɵmer is
wired to operate only when the compressor is in operaƟon and the thermostat is closed. Although
defrost funcƟon is generally an issue in refrigeraƟon units, heat pump air condiƟoning systems
require periodic defrosƟng of the outdoor coil under certain condiƟons. Electronic defrost controls
may be used in place of mechanical controls, providing precise control without moving parts. Defrost
Ɵmer controls for commercial equipment have a means to automaƟcally advance the Ɵmer back to
the run cycle before the Ɵme sequence if defrost temperature is saƟsfied.
THERMOSTATS
A thermostat is a temperature‐sensiƟve switch. Some thermostats are designed to operate at low
voltage, generally 24 volts, while others are designed for high voltage and are connected directly to
motors or heaƟng units. Low‐voltage thermostats are more economical and safer to use inside the
home.
A residenƟal air condiƟoning system thermostat controls three major components:
Compressor
Condenser fan (comes on with the compressor)
Evaporator fan motor or blower
A residenƟal heaƟng system thermostat controls one major component:
HeaƟng (sequencer, gas valve, or electronic control board)
Fig. 2‐30: DomesƟc refrigeraƟon defrost Ɵmer circuit