Electrical Theory & Applications for HVACR
Chapter 3: Motors
Page 67
FULL LOAD AMPS (FLA)
Full load amps (FLA) or rated run load amps (RLA) refers to the amperage a motor draws when at
normal speed and fully loaded. Most inducƟon motors operate at less than FLA because the motor is
rarely working at fully loaded condiƟons. Overload occurs when amperage exceeds a percentage of
the FLA raƟng or motor heat gets to high.
OVERLOAD PROTECTORS
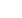
An overload protector is a device that protects a motor
against overload condiƟons. There are a variety of
overload protector types, and the type commonly used
depends on the type of motor and its applicaƟon. It is
common for a fracƟonal horsepower, single‐phase AC
motor to have an overload with a snap‐acƟng bimetal disc
that makes and breaks a set of contacts. Excessive
current causes the bimetal disk to deflect and open the
circuit. When cooled, the disc returns to the closed
posiƟon.
Repeated opening and closing of the overload is called cycling. ConƟnuous overload cycling is a
warning that the motor is in danger of a burnout. It is important to isolate and repair the cause of
the overload to prevent damage to the motor.
Another type of overload protector is an internal overload protector located inside the motor
windings. When checking motor windings, do not condemn the motor unƟl allowing sufficient Ɵme
for the internal overload to reset. The overload is acƟvated by temperature and current and may
take four to eight hours to reset.
When servicing a motor that has tripped on overload, be sure to disconnect it from the
power source. The motor could suddenly restart when the overload resets.
THREE-PHASE MOTORS
Three‐phase motors are very common in commercial and industrial applicaƟons. They are smaller
and more efficient than single‐phase motors of equal horsepower. Three‐phase motors have high
starƟng torque and high running torque, without the use of start windings or capacitors.
For proper operaƟon, all three supply wires (L1, L2, and L3) must be
connected to the motor terminals. The safety ground (green) wire is
included for equipment ground. This grounding wire is connected to the
motor frame to provide an escape for electrons in case the motor
windings become shorted to the metal frame.
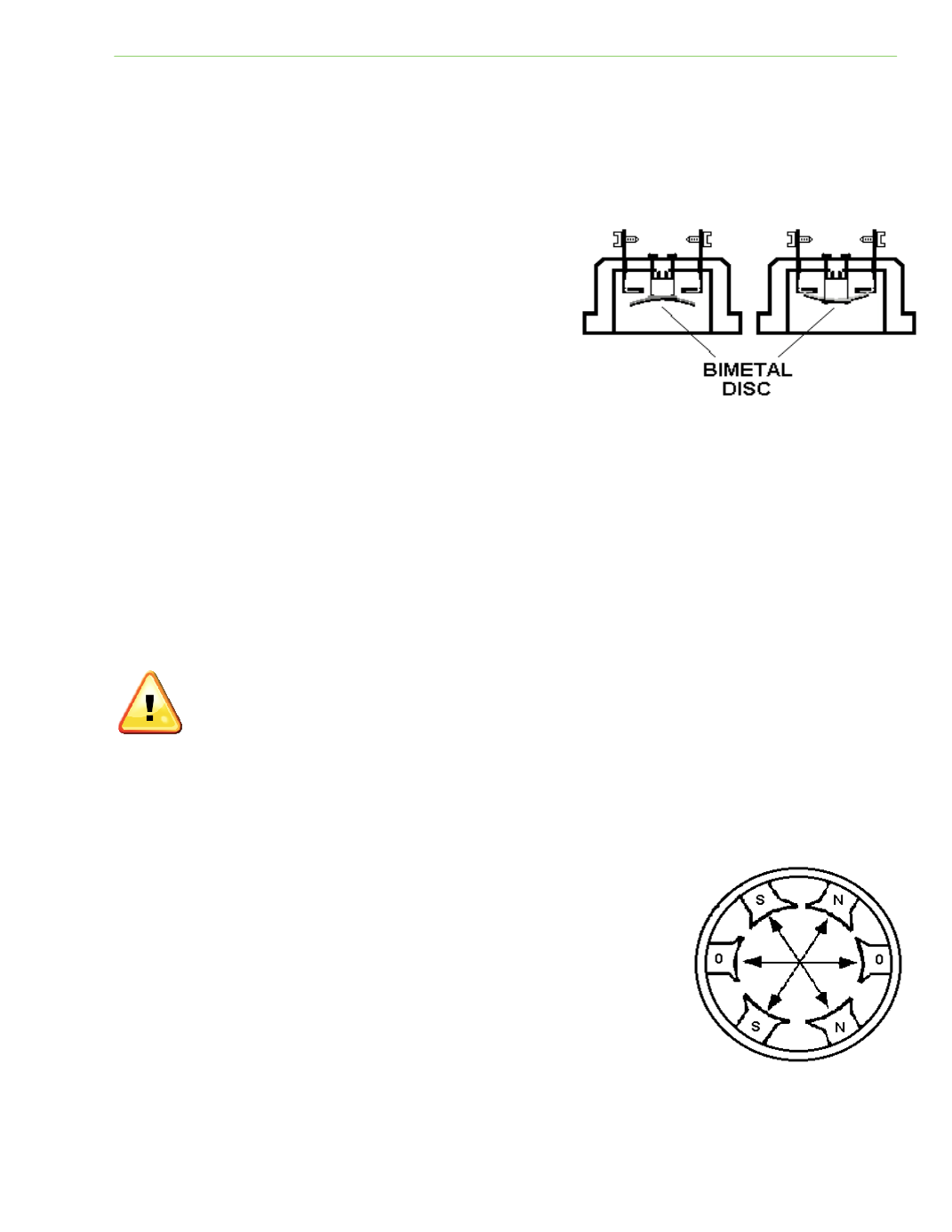
Three‐phase motors have three pairs of stator poles; one pair for each
supply wire. Each winding produces a north and south pole; this is called
one pole per phase. A typical three‐phase motor has three pairs of
stator poles, meaning three north and three south poles. Each north and
south combinaƟon is located directly opposite another. These poles are
equally spaced in a circle, exactly 60 degrees apart.
Fig. 3‐28: Overload protectors use a snap‐
acƟng bimetal disc to break a set of contacts
Fig. 3‐29