Page 24
Chapter 2: Circuits and Their Components
Electrical Theory & Applications for HVACR
INSULATORS
Insulators are materials that offer high resistance to electron flow. Materials that have 5 or more
electrons in the outer orbit are considered insulators. There is no perfect insulator. Insulators can
break down due to moisture, heat, excess current flow, vibraƟon, chemicals, etc. InsulaƟon can be
heat resistant, moisture resistant, oil resistant, etc. The type of insulaƟon or covering determines
where the conductor can be safely used. Always use care to avoid damaging the insulated covering on
the wire.
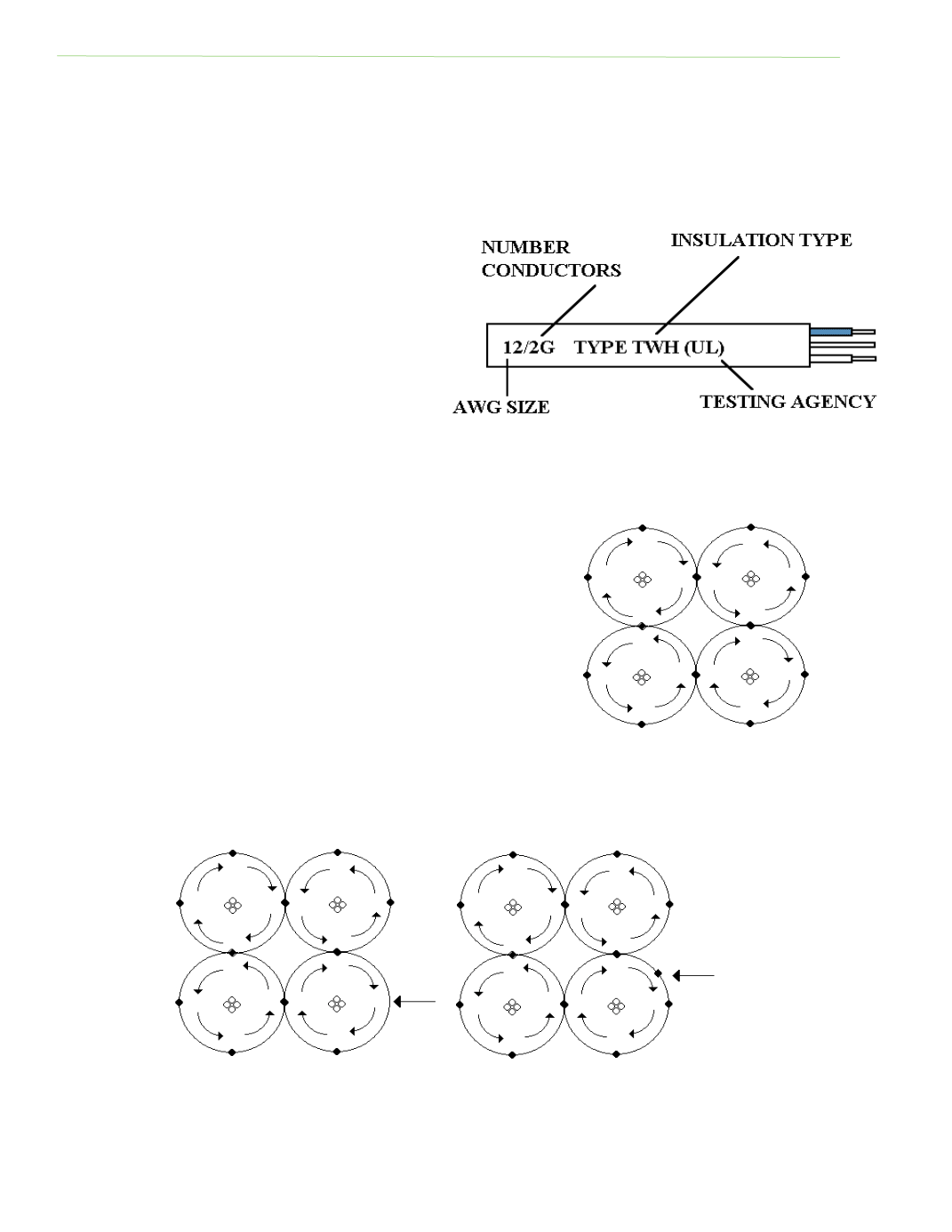
The manufacturers of electrical wires use leƩer
codes to designate the type of insulaƟon on a
wire. InsulaƟon types are coded by leƩers of
the alphabet and stamped on the insulaƟon
surface. The most commonly used types are
TW, THN, TFF, or THWN.
Consult the NEC handbook for a complete list
of insulaƟon types. Figure 2‐10 shows how
conductor insulaƟon is marked.
SEMI-CONDUCTORS
A semi‐conductor is a material that has electrical properƟes of
current flow between a conductor and an insulator (four
electrons in the valance ring.) Silicon is an example of such
material. Pure silicon is not a good conductor because it has
four electrons in its outer orbit that bond with other silicon
atoms to form a stable crystal.
The outer ring of a silicon atom has four electrons, but there is
room for eight. Electrons share orbits with other atoms to form
covalent bonds. If an impurity with either three or five
electrons in the outer orbit is added to silicon, the crystalline
structure will have either an excess electron or a hole and can become a conductor or insulator if the
correct voltage and polarity are applied. The new structure is called P‐Type or N‐Type material.
P‐Type Material (Missing 1 Electron)
N‐Type Material ( 1 Extra Electron)
Fig. 2‐11: Silicon atoms
Fig. 2‐10: InsulaƟon informaƟon
Fig. 2‐12: P‐Type and N‐Type material